What’s the cost of ignoring cybersecurity risks for a small business?
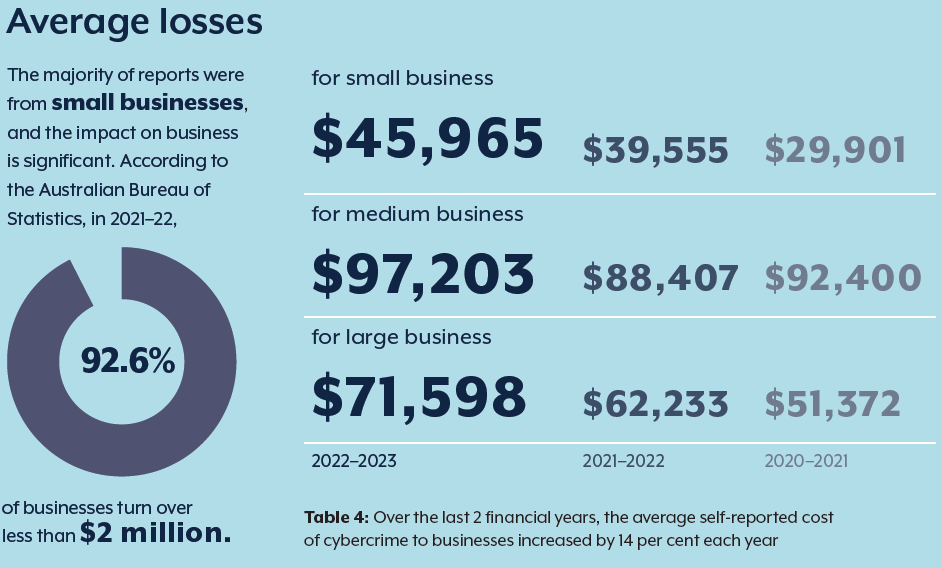
Many small businesses overlook cybersecurity, often assuming that attackers only target larger companies. However, ignoring cybersecurity risks can have severe financial and operational consequences. From direct financial losses to lasting damage to reputation and customer trust, the cost of a cyber incident can be far-reaching and difficult to recover from. Below, we explore the hidden and obvious costs associated with neglecting cybersecurity and explain why proactive investment in security is essential for small businesses.
1. Direct Financial Losses
Description: Cyberattacks often result in immediate financial costs, particularly when dealing with ransomware attacks, where a business may have to pay a ransom to regain access to their own data.
Examples of Direct Costs:
- Ransomware Payments: Some small businesses choose to pay attackers to regain data access, which can be a costly choice.
- Fraud and Theft: Cybercriminals who gain access to payment systems or sensitive data can conduct fraud, draining funds directly from business accounts.
- Loss of Business Revenue: If systems go offline, businesses experience lost revenue due to halted operations, which can take days or even weeks to resolve.
Long-Term Effects: The financial hit from a cyberattack can take months or years to recover, impacting budgets and limiting the business’s ability to grow.
2. Loss of Customer Trust and Reputation
Description: Cyber incidents often result in breaches of customer data, eroding trust and damaging a company’s reputation. For small businesses, reputation is a critical asset that is challenging to rebuild once damaged.
How It Impacts Small Businesses:
- Decreased Customer Loyalty: Clients are less likely to return to a business that has compromised their data.
- Negative Publicity: Data breaches are often publicly reported, which can lead to negative media coverage and harm the business’s brand image.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Potential customers may opt for competitors perceived as more secure, especially if the business’s breach history is widely known.
Solution: Regularly communicate with customers about data protection measures, and reinforce the value your business places on customer privacy and security.
3. Legal and Regulatory Penalties
Description: Small businesses often fail to realize that non-compliance with cybersecurity laws and regulations can lead to significant fines and penalties, especially if they handle sensitive customer data.
Common Regulatory Costs:
- Fines for Data Breaches: Many jurisdictions impose fines on businesses that fail to protect personal data. Regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA have strict compliance requirements, and penalties can be substantial.
- Legal Fees: Businesses may incur legal fees to address class-action lawsuits or settle cases with affected customers.
- Investigation Costs: In many cases, businesses must fund an investigation to understand the breach’s scope, adding to the costs associated with regulatory compliance.
Proactive Measure: Maintain a comprehensive cybersecurity policy that includes compliance with relevant industry regulations and regularly review policies to ensure alignment with evolving standards.
4. Operational Downtime and Productivity Losses
Description: Cyber incidents often lead to system outages, leaving employees unable to perform their work. This downtime can affect productivity across the entire company, disrupting critical business functions.
Productivity Loss Examples:
- Employee Idle Time: When key systems are down, employees may be forced to wait until systems are restored, wasting hours or even days.
- Resource Allocation: IT and administrative teams must shift their focus to managing the incident, delaying other projects and business priorities.
- Supply Chain Impact: A cyber incident can have a domino effect, causing delays in product delivery, customer service, and other essential functions.
Best Practice: Ensure regular data backups and maintain a tested incident response plan to reduce downtime in the event of an attack.
5. Cost of Recovery and System Upgrades
Description: After a cyber incident, businesses often have to invest in new systems, security software, or even bring in external cybersecurity experts to fix vulnerabilities and prevent future breaches.
Recovery Costs:
- Forensics and IT Services: Post-attack forensics are often necessary to assess the extent of damage and may require hiring specialists.
- System Replacement: Damaged or compromised systems may need to be replaced entirely, especially if they have been compromised by malware.
- Increased Insurance Premiums: Cyber incidents can result in higher premiums or even denial of coverage, adding to the long-term costs.
Proactive Investment: Regularly updating and auditing systems for vulnerabilities is much cheaper than dealing with the fallout of an attack. Consider partnering with a managed IT provider to streamline ongoing security needs.
6. Emotional and Psychological Costs
Description: Cyberattacks can also bring emotional strain on business owners and employees, particularly in small businesses where teams are more tight-knit and closely involved in the company’s day-to-day operations.
Impact on Team Morale:
- Stress and Burnout: Incident recovery can be exhausting, particularly for small teams. Cyber incidents can result in longer work hours, increased stress, and burnout.
- Loss of Confidence: Employees may feel insecure about their own data privacy, impacting morale and productivity.
- Strained Customer Relations: Addressing customer concerns post-breach adds emotional strain as teams work to reassure and regain trust.
Solution: Building a supportive work culture around cybersecurity awareness can help reduce anxiety and instill confidence. Regular training and open communication regarding security practices can empower employees to be proactive in preventing incidents.
Conclusion: Investing in Cybersecurity for Long-Term Business Stability
For small businesses, the cost of ignoring cybersecurity risks is far greater than the upfront expense of preventive measures. Cyber incidents carry a wide range of financial, operational, legal, and emotional costs that can challenge even the most resilient businesses.
Investing in cybersecurity is not just about technology; it’s about safeguarding your business’s future, reputation, and relationships with customers. A proactive approach to cybersecurity can prevent costly incidents and give small business owners peace of mind, knowing their operations and data are well-protected against today’s evolving cyber threats.

